Fractures of the wrist and hand are common injuries that can occur due to various causes. Understanding the different types of fractures and their associated symptoms is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. This article will provide an overview of the most common wrist and hand fractures, including their anatomy, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding Wrist and Hand Fractures
Fractures in the wrist and hand can occur in different bones and joints. To comprehend these injuries better, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the wrist and hand.
Anatomy of the Wrist and Hand
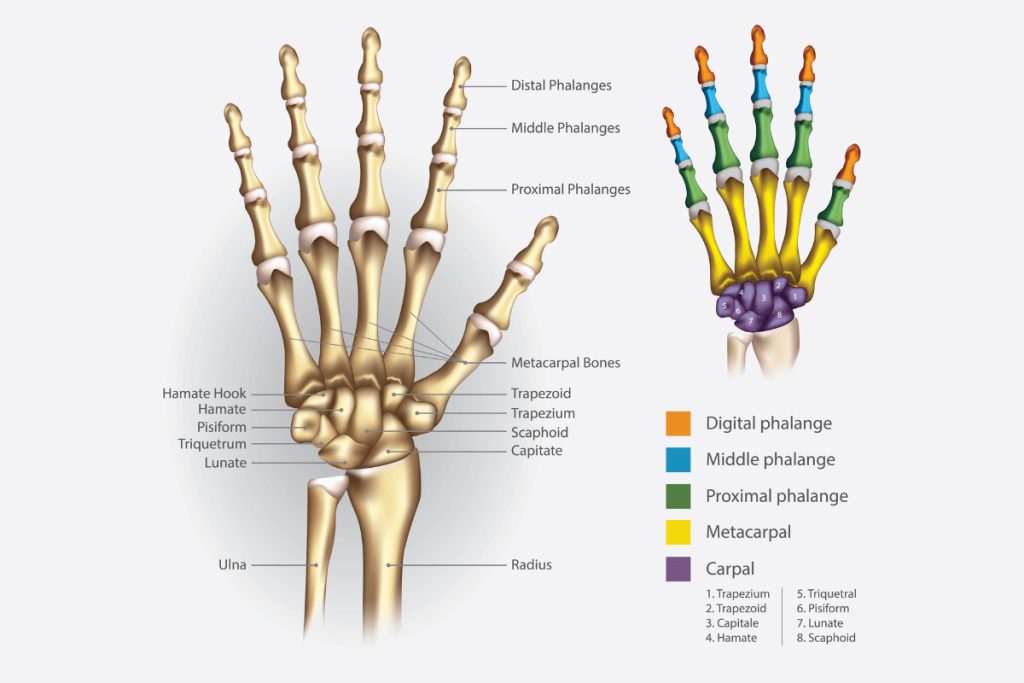
The wrist consists of eight small bones known as carpals, while the hand is composed of metacarpal bones and phalanges. These bones work together to provide stability and flexibility, enabling us to perform a wide range of daily activities.
The carpals, which are located in the wrist, form two rows. The proximal row consists of the scaphoid, lunate, triquetral, and pisiform bones. These bones are responsible for connecting the forearm to the hand and play a crucial role in wrist movements. The distal row, on the other hand, consists of the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones. These bones provide support and stability to the hand, allowing us to grasp and manipulate objects with precision.
Moving on to the hand, the metacarpal bones are long bones that connect the carpals to the phalanges. There are five metacarpals, numbered from one to five starting from the thumb side. Each metacarpal has a base, shaft, and head. The heads of the metacarpals form the knuckles, which are essential for gripping and performing fine motor tasks.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fractures

Fractures in the wrist and hand can be caused by various factors, including falls (also known as a FOOSH – fall onto an outstretched hand), sports injuries, and accidents. These injuries often occur when a significant force is applied to the bones, causing them to break or crack. Additionally, certain risk factors can make individuals more prone to fractures.
Osteoporosis, a condition characterised by weak and brittle bones, is a significant risk factor for fractures. As bones become more fragile, even minor falls or accidents can lead to fractures. It is crucial for individuals with osteoporosis to take preventive measures and protect their wrists and hands from potential injuries.
Repetitive stress injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, can also increase the risk of fractures in the wrist and hand. These injuries often occur due to repetitive motions or prolonged periods of stress on the joints and bones. Over time, the constant strain can weaken the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures.
By understanding the anatomy of the wrist and hand, as well as the causes and risk factors of fractures, we can take steps to prevent these injuries and maintain the health and functionality of our wrists and hands.
Types of Wrist Fractures
Wrist fractures are the most common type of hand and wrist injury and often result from trauma or falls onto an outstretched hand (FOOSH). The following are some of the most common types of wrist fractures:
Scaphoid Fracture
The scaphoid bone is susceptible to fractures, especially during falls on the hands. It is one of the most common wrist fracture types. Symptoms of a scaphoid fracture may include pain, swelling, and difficulty gripping objects. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications such as avascular necrosis.
Find out more in our comprehensive guide to scaphoid fractures.
Distal Radius Fracture
A distal radial fracture occurs when the larger of the two forearm bones, the radius, breaks near the wrist joint. This type of fracture can cause pain, swelling, and wrist deformity. Treatment may involve immobilisation with a cast or, in some cases, surgery.
Ulna Fracture
The ulna bone, which runs alongside the radius, can also fracture. This type of fracture, known as an ulnar fracture, can cause pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. Treatment typically involves immobilisation and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
It is important to note that wrist fractures can vary in severity and complexity.
Other Types of Less Common Wrist Injuries
In addition to the common types of fractures mentioned above, other less common injuries can occur in the wrist. When the ligament between the scaphoid and lunate bones tears, it is known as scapholunate dissociation, while perilunate dislocation refers to the displacement of the wrist bones from their normal positions.
Diagnosing Wrist Fractures
When it comes to diagnosing wrist fractures, medical professionals employ various imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These imaging tests help determine the exact location and extent of the fracture, allowing for appropriate treatment planning.
Treatment for wrist fractures depends on several factors, including the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and lifestyle. In some cases, non-surgical methods such as immobilisation with a cast or splint, pain management, and physical therapy may be sufficient for a full recovery. However, more complex fractures may require surgical intervention, which can involve the use of plates, screws, or external fixation devices to stabilise the bones during the healing process.
Types of Hand Fractures
In addition to wrist fractures, fractures can also occur in the bones of the hand. It’s important to understand the different types of hand fractures to properly diagnose and treat them. Let’s take a closer look at the two main types:
Metacarpal Fracture
A metacarpal fracture is a break in one of the long bones of the hand that connects the fingers to the wrist. These fractures can occur as a result of a direct blow to the hand, such as during a fall or a sports-related injury. The symptoms of a metacarpal fracture may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected finger. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect a metacarpal fracture, as proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for a successful recovery.
Treatment options for metacarpal fractures depend on the severity of the fracture. In some cases, a simple fracture may only require immobilisation with a cast or splint. However, more complex fractures may require surgical intervention to realign the bones and ensure proper healing. Your physio or doctor will evaluate your specific case and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
Phalange Fracture
Phalange fractures involve breaks in the bones of the fingers or thumb. These fractures can occur due to a variety of reasons, including falls, crushing injuries, or direct trauma to the hand. The symptoms of a phalange fracture may include pain, tenderness, and difficulty bending or straightening the affected finger. It’s important to note that even a seemingly minor fracture can lead to long-term complications if not treated properly.
The treatment for phalange fractures varies depending on the location and severity of the fracture. In some cases, a simple fracture may heal with conservative measures such as splinting or buddy taping, where the injured finger is taped to an adjacent finger for support. However, more complex fractures may require surgical intervention to realign the bones and ensure proper healing. Your doctor will assess your specific case and recommend the most suitable treatment approach.
Expanding on the topic of hand fractures allows us to delve deeper into the intricacies of each type, providing a more comprehensive understanding of these injuries. Remember, if you suspect a hand fracture, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Wrist and Hand Fractures
Recognising the symptoms and seeking a proper diagnosis are crucial for effective treatment of wrist and hand fractures.
When it comes to wrist and hand fractures, it’s important to pay attention to the common symptoms that may indicate a fracture has occurred. One of the most noticeable symptoms is pain. The affected area may throb or ache, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. Alongside pain, swelling and tenderness are often present. The injured area may become swollen and feel tender to the touch, causing discomfort and limited mobility.
Another symptom to be aware of is bruising. Fractures can cause blood vessels to rupture, resulting in a bruised appearance around the injured area. This discolouration can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the fracture. Additionally, deformity may be evident in some cases. The affected wrist or hand may appear misaligned or out of its normal shape, indicating a more severe fracture.
Furthermore, individuals with wrist and hand fractures may experience difficulty moving the affected area. Simple tasks like gripping objects or making a fist can become challenging due to the pain and limited range of motion. In certain instances, numbness or tingling sensations may also be present. This can occur when nerves are affected by the fracture, causing abnormal sensations in the surrounding areas.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing wrist and hand fractures usually involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and a detailed assessment of the patient’s medical history. During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will carefully assess the injured area, looking for signs of swelling, tenderness, deformity, and limited mobility.
Imaging tests play a crucial role in determining the location and severity of the fracture. X-rays are commonly used to visualise the bones and identify any fractures or dislocations. They provide detailed images that help healthcare professionals make an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be recommended to further evaluate the soft tissues surrounding the fracture.
Additionally, a detailed assessment of the patient’s medical history is essential in diagnosing wrist and hand fractures. Understanding any previous injuries, underlying medical conditions, or activities that may have contributed to the fracture can provide valuable insights for the healthcare professional. This information helps guide the appropriate treatment plan, ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient.
Treatment Options for Wrist and Hand Fractures
The specific treatment approach for wrist and hand fractures depends on various factors, including the type and location of the fracture, its severity, and the individual patient’s age and overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatment options for wrist and hand fractures may include immobilisation with a splint or cast, pain management, physical hand therapy, and regular follow-up visits to monitor the healing process.
Read our guide to hand therapy and therapists.
Surgical Treatments

In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the fractured bones and restore proper function. Surgical treatments may involve the use of internal fixation devices such as plates, screws, or pins to stabilise the fracture and facilitate healing.
It is crucial to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan and follow the healthcare provider’s instructions during the recovery period to achieve optimal outcomes and prevent potential complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wrist and hand fractures are common injuries with various types and causes. Recognising the symptoms, obtaining a timely diagnosis, and receiving appropriate treatment are essential for a successful recovery and restoration of hand function. If you suspect a wrist or hand fracture, it is crucial to seek prompt medical attention to prevent further damage and ensure the best possible outcome.
Find out more about how our specialist hand therapy service can help you achieve the best possible treatment outcome for your hand, wrist or forearm condition.
You can book an appointment if you’d like to see one of our Advanced Hand Specialist Physiotherapists or contact us to discuss your needs.




Comments